What Is Slag Inclusion in Welding
Slag inclusion in welding refers to the presence of nonmetallic particles trapped in the weld or between layers.
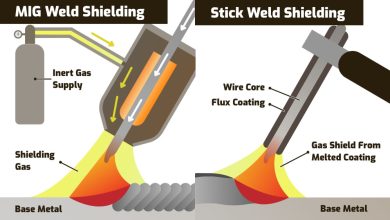
Slag is formed when flux melts into or on top of the weld area during welding and solidifies as the weld cools.
It is composed of carbonate and silicate materials that shield the weld from atmospheric gases and prevent oxidation.
Slag inclusions can cause concentrated stress and reduce the durability of the weld metal.
They can also lead to corrosion over time and affect the reliability and quality of the weld joint.
Slag inclusions are commonly seen in different welding methods such as MMA, FCA, submerged arc welding, and MIG welding.
To prevent slag inclusions, proper electrode manipulation, correct electrode size and angle, and smooth weld bead profiles are important.
Removal of slag between runs using grinding, light chipping, or wire brushing is also necessary.
Different cleaning tools may be required for different materials.
Did You Know?
Trivia 1: Did you know that slag inclusion in welding refers to the presence of non-metallic materials, such as oxides or other impurities, trapped within the weld metal?
Trivia 2: In some cases, tiny air bubbles can also get trapped in the weld metal, resulting in a similar defect known as gas porosity or gas inclusion.
Trivia 3: Slag inclusion can negatively affect the strength and integrity of a weld, making it susceptible to cracking or failure under stress.
Trivia 4: Interestingly, the term “slag” derives from the Old Norse word “sleggja,” meaning to strike or hit, which refers to the process of removing the slag from the welded joint.
Trivia 5: To prevent slag inclusion during welding, techniques such as proper electrode manipulation, controlling heat input, and maintaining suitable welding parameters are employed to ensure high-quality welds.
Formation And Composition Of Slag In Welding
Slag formation is a common occurrence in welding processes. It occurs when the flux used in welding melts into or on top of the weld area. The flux serves as a protective shield against atmospheric gases and oxidation.
As the weld area cools during the welding process, the remaining flux solidifies and forms a layer called slag. This slag acts like a crust that covers the weld bead. It is essential to understand that slag is a nonmetallic material and can cause various issues if present in the weld.
The composition of the flux used significantly influences the formation of slag. Different flux compositions have different melting points and behaviors during welding. For instance, using a flux that contains iron oxide can help prevent the formation of slag inclusions.
Key Points:
- Slag formation is common in welding.
- Flux melts and forms slag.
- Slag acts as a protective layer on the weld bead.
- Slag is nonmetallic and can cause problems if present in the weld.
- Flux composition affects slag formation.
- Flux with iron oxide can help prevent slag inclusions.
“Flux serves to shield the weld from atmospheric gases and prevent oxidation.”
Impact Of Slag Inclusions On Weld Quality And Durability
Slag inclusions are nonmetallic particles that become trapped within the weld or between layers of the weld. These inclusions can cause concentrated stress points within the weld, reducing its overall durability. Over time, slag inclusions can lead to corrosion in the weld, further compromising its integrity.
The presence of slag inclusions affects the quality and reliability of the weld joint. If not properly addressed, slag can weaken the weld and potentially lead to weld failure.
To prevent and mitigate the occurrence of slag inclusions, it is crucial to take necessary precautions including:
- Ensuring proper cleaning and removal of slag from the welding surface before and after welding
- Using appropriate welding techniques to minimize the formation of slag inclusions
- Monitoring and inspecting the weld for any signs of slag inclusions during and after the welding process
- Performing non-destructive testing to detect the presence of slag inclusions
- Implementing strict quality control measures to verify the absence of slag inclusions.
It is important to note that proper training and knowledge of welding processes are essential in identifying and preventing the formation of slag inclusions.
Slag inclusions can have detrimental effects on the weld joint, compromising its strength and durability. By taking necessary precautions and being vigilant during the welding process, the occurrence of slag inclusions can be minimized, ensuring a high-quality and reliable weld joint.
Factors Affecting The Risk Of Slag Inclusions
Several factors increase the risk of slag inclusions in welding. One crucial factor is the composition of the flux coating. The type of flux used also plays a role. Certain flux compositions may be more prone to forming slag inclusions, while others may be designed to reduce this risk.
In addition to flux composition, various welding parameters and techniques can impact the occurrence of slag inclusions. Proper electrode manipulation, including maintaining the correct size and angle, is essential. Smooth weld bead profiles and adequate overlap of adjacent weld beads are also important factors in preventing slag inclusions.
Lastly, the type of welding process used can affect the risk of slag inclusions. Slag inclusions are commonly observed in processes such as:
- Manual Metal Arc (MMA)
- Flux-Cored Arc (FCA)
- Submerged Arc Welding
- Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding
Understanding the specific considerations and risks associated with each welding process can help minimize the occurrence of slag inclusions.
Prevention And Mitigation Of Slag Inclusions
Preventing and Mitigating Slag Inclusions
To ensure high-quality weld joints, it is crucial to prevent and mitigate slag inclusions. This can be achieved through a combination of proper welding techniques and equipment selection. Here are some key factors to consider:
-
Handling the electrode correctly: Proper electrode handling techniques are essential in preventing slag inclusions. This includes proper storage, avoiding moisture, and ensuring the electrode remains dry and clean during welding.
-
Selecting the appropriate electrode size: Choosing the right electrode size for the specific welding task is important. Using an electrode that is too large may result in excessive heat input, while using an electrode that is too small can lead to insufficient penetration.
-
Maintaining the proper welding angle: Maintaining the correct welding angle helps in achieving good weld penetration and prevents the entrapment of slag. It is recommended to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the optimal welding angle.
-
Planning for multiple passes: When dealing with thicker materials or complex joint designs, planning for multiple passes is necessary. This allows for proper deposition of weld metal and helps prevent slag inclusions by ensuring full fusion throughout the joint.
-
Using the appropriate amperage settings: Correctly setting the welding current, or amperage, is vital for preventing slag inclusions. Insufficient amperage may lead to incomplete fusion, while excessive amperage can result in excessive spatter and slag.
It is also important to invest in a high-quality welding machine and ensure its proper maintenance. By doing so, potential issues can be minimized, and the risk of slag inclusions can be reduced. Regular maintenance and calibration of the welding machine contribute to the overall quality of the weld joints.
In the event that slag inclusions do occur, prompt action should be taken to remove them. Various methods can be used, including grinding, light chipping, or wire brushing, depending on the materials being welded. It is crucial to use the appropriate cleaning tools to effectively remove the slag between runs.
Remember, preventing and mitigating slag inclusions require attention to detail, proper technique, and the use of suitable equipment. By following these guidelines, welders can minimize the occurrence of slag inclusions and achieve high-quality weld joints.
- Proper electrode handling techniques
- Appropriate electrode size selection
- Maintaining the correct welding angle
- Planning for multiple passes
- Using the appropriate amperage settings
“Investing in proper welding techniques and equipment helps in preventing slag inclusions.”
Cleaning And Standards For Slag Inclusions In Welds
Cleaning of slag inclusions in welds is crucial to ensure the integrity and quality of the weld joint. Different industries and applications may have specific standards and codes that dictate the acceptable levels of slag and flux inclusions in the final weld.
Following the appropriate cleaning procedures and adhering to the relevant standards helps to maintain the desired weld quality. Welding professionals should familiarize themselves with the specific requirements and guidelines related to slag inclusions in their respective industries to ensure compliance and produce high-quality welds.
Slag inclusions are nonmetallic particles that can become trapped in the weld or between layers, compromising the quality and durability of the weld joint. The risk of slag inclusions can be influenced by factors such as the flux composition, welding techniques, and equipment selection. By implementing proper prevention and mitigation measures, such as correct electrode manipulation and electrode selection, slag inclusions can be minimized. Additionally, regular cleaning and adherence to applicable standards are essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of weld joints.
Check this out:
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you prevent slag inclusion?
To prevent slag inclusion, it is crucial to employ effective welding techniques that result in smooth weld beads and ensure sufficient inter-run fusion. This helps prevent the formation of pockets that may trap slag. Additionally, it is important to adjust the current and travel speed correctly to avoid undercutting the sidewall, as this can make the removal of slag challenging. By closely adhering to these practices, the risk of slag inclusion can be significantly reduced during the welding process.
What is the effect of slag inclusion in welding?
The presence of slag inclusion in welding has a detrimental effect on the quality and durability of the weld metal. These inclusions cause concentrated stress, which compromises the structural integrity of the welding joint. Furthermore, the presence of slag inclusions can initiate corrosion in the weld, gradually weakening its strength and compromising its longevity. In some cases, the presence of slag inclusions can even lead to the formation of crevices, which further exacerbate the corrosion process by providing additional surface area for it to occur. Consequently, eliminating or minimizing slag inclusions is crucial to ensure the long-term reliability and performance of welded structures.
What is slag porosity in welding?
Slag porosity in welding refers to the presence of cavities in the weld metal caused by the entrapment of slag during the welding process. When welding, slag is formed as a byproduct of the flux or shielding gas used. If the slag is not effectively removed or dispersed, it can become trapped within the weld, resulting in slag porosity. This type of porosity appears as distributed pores within the weld metal and can compromise its integrity. It is essential to properly manage and remove slag during welding to prevent the formation of slag porosity and ensure a sound weld.
What is slag inclusion in casting defect?
Slag inclusion in casting defect refers to the occurrence of non-metallic materials, such as slag, within the casting, creating internal defects. These defects can compromise the quality and integrity of the castings, making it crucial to prevent slag inclusion. By carefully monitoring and controlling the casting process, ensuring proper melting and refining techniques, and employing effective slag removal methods, manufacturers can minimize the occurrence of slag inclusion and ensure the production of high-quality castings.