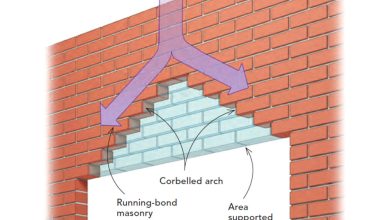
What Is Masonry Structure
A masonry structure is a construction made using materials such as brick, stone, or concrete blocks combined with mortar.
Masonry has been used for centuries and can be seen in historical landmarks like the Egyptian pyramids, Roman aqueducts, and medieval cathedrals.
It can be used for both structural and non-structural purposes.
Common types of masonry include brick and concrete block.
Masonry offers advantages such as increased thermal mass and fire protection.
Masonry structures are typically built with blocks or bricks connected with a layer of mortar, but dry set masonry, where the blocks rely on friction for strength, is also used.
Stone masonry can be done with dressed stones or irregularly shaped stones.
Concrete masonry units or blocks are commonly used for constructing walls in various types of buildings.
Masonry associations can provide additional resources for further information.
Did You Know?
1. The Great Wall of China, often referred to as a masonry structure, is made up of over 3 million individual bricks and stones, some of which were placed as early as the 7th century BC.
2. The largest masonry dome in the world is the Pantheon in Rome, which has a diameter of 43.3 meters (142 feet). It was built in 118-128 AD and remains the largest unsupported dome to this day.
3. One of the most remarkable masonry structures in the Americas is Machu Picchu, an ancient Incan city located in Peru. The stones used to construct this astounding citadel were cut with such precision that no mortar was required for their perfect fit.
4. The iconic Taj Mahal in India, renowned for its intricate masonry work, is constructed with a technique known as “pietra dura.” This involves inlaying semi-precious stones, such as lapis lazuli and amethyst, onto the marble to create beautiful patterns and designs.
5. The Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, located in Rome, was once the largest masonry temple in the Roman Republic. Unfortunately, it was destroyed by several fires throughout history and now exists only as ruins, but its sheer size and grandeur were considered awe-inspiring in ancient times.
Introduction To Masonry Construction
Masonry is a construction craft that involves building structures with materials such as brick, stone, or concrete blocks combined with mortar. It has been used for centuries and is known for its durability and strength. Masonry structures are typically made up of blocks or bricks connected with a thin layer of mortar. This technique creates a solid and resilient structure that can withstand various environmental conditions.
One of the key features of masonry construction is the use of mortar. Mortar acts as a binding agent that holds the individual masonry units together, creating a unified and stable structure. It is typically made by mixing cement, sand, and water to create a paste-like substance. The mortar then hardens over time, providing additional strength to the overall masonry structure.
Examples Of Masonry Throughout History
- Masonry has a rich history and is evident in architectural marvels across different civilizations.
- Egyptian pyramids are examples of masonry structures, built with massive stone blocks.
- Roman aqueducts combined stone and brick in their construction.
- Medieval cathedrals used finely crafted stone blocks.
These historical examples demonstrate the long-lasting and enduring nature of masonry construction. Despite their age, these structures are still standing today, showcasing the durability and timelessness of masonry.
Structural And Non-Structural Applications Of Masonry
Masonry is a versatile construction method that finds applications in both structural and non-structural projects.
For structural purposes, masonry is employed to create load-bearing walls and support structures. The inherent strength of masonry materials makes them well-suited for constructing buildings and other structures that demand stability and durability.
In addition to structural uses, masonry also serves non-structural purposes such as decorative walls, fireplaces, and retaining walls. These applications harness masonry’s aesthetic appeal and its capacity to withstand high temperatures.
Common Types Of Masonry Materials
Brick and Concrete Block
Brick and concrete block are two common types of masonry materials. Brick is highly versatile and enduring, making it a popular choice. It comes in various sizes, shapes, and colors, allowing for creative architectural designs. On the other hand, concrete block, also known as concrete masonry units (CMUs), is widely used due to its strength, durability, and ease of use.
Stone Masonry
Stone masonry is another option, which can be done with dressed stones (known as ashlar masonry) or with irregularly shaped stones (referred to as rubble masonry). Ashlar masonry offers a more refined and polished appearance, while rubble masonry showcases a natural and rustic look.
Advantages And Unique Features Of Masonry Structures
Masonry structures offer several advantages over other construction methods.
One advantage is increased thermal mass, which helps regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing and releasing heat slowly. This can contribute to energy efficiency and reduce heating and cooling costs in buildings.
Additionally, masonry provides excellent fire protection. Brick and concrete block walls have high fire resistance, making them a safe choice for structures that require fire-rated walls.
Another unique feature of masonry is the ability to create dry set masonry structures. Dry set masonry does not use mortar and instead relies on the friction between interlocking blocks for strength. This technique offers flexibility and ease of construction without compromising structural integrity.
Masonry construction is a versatile and enduring craft that has been utilized for centuries.
Its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice for various types of structures. From ancient Egyptian pyramids to modern architectural designs, masonry has stood the test of time and continues to be a fundamental construction technique.
For further information and resources on masonry construction, interested individuals can consult masonry associations such as the Masonry Contractors of America or the International Masonry Institute. These associations provide valuable insight into best practices, industry standards, and the latest advancements in the field of masonry.
– Increased thermal mass
– Excellent fire protection
– Dry set masonry offers flexibility and ease of construction
– Masonry is versatile, enduring, and aesthetically appealing
Check this out:
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the masonry structure?
A masonry structure refers to a building or a construction made by assembling individual units, such as bricks, stones, or concrete blocks, and binding them together with mortar. This well-established construction technique is widely used globally due to the numerous advantages it offers. Masonry structures are known for their durability, strength, and resilience, making them ideal for various types of buildings, from residential homes to commercial complexes. The use of materials like brick, stone, and concrete blocks in masonry not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the structure but also provides excellent thermal and sound insulation properties. With its versatility and long-lasting attributes, masonry continues to be a favored choice in construction projects worldwide.
What do you mean by masonry?
Masonry refers to the skillful practice of constructing and shaping structures using various materials such as stone, clay, brick, or concrete block. This art and craft involve the meticulous building and fabrication techniques to create durable and aesthetically appealing structures. It encompasses not only the traditional use of stones and bricks but also includes the construction of poured concrete that can either be reinforced or unreinforced, thus broadening the scope of masonry. With its diverse applications, masonry plays a crucial role in shaping the architectural landscape.
What is an example of masonry structures?
One example of masonry structures is a load-bearing wall, which is commonly used in construction. Load-bearing walls support the weight of the building by transferring the load from the roof or floor above to the foundation below. These walls are typically made of brick or stone and provide structural integrity to the overall building. Another example is a masonry fireplace, which not only adds aesthetic appeal but also serves its functional purpose of providing heat and ambiance. These fireplaces are constructed using fire-resistant materials such as firebricks or refractory bricks to withstand high temperatures while ensuring safety.
What is masonry as a structural material?
Masonry, as a structural material, encompasses the art of constructing buildings by bonding building units together using mortar. These building units can vary from bricks and stones to precast blocks of concrete. Masonry is commonly employed in the construction of foundational elements, walls, columns, and other key structural components within buildings. Its time-honored techniques and enduring qualities make masonry a trusted choice for creating sturdy and durable structures that stand the test of time.